As more people switch to macOS, hackers are finding more ways to attack these users with malware. Although macOS is considered safer than other operating systems, it is not immune to threats.
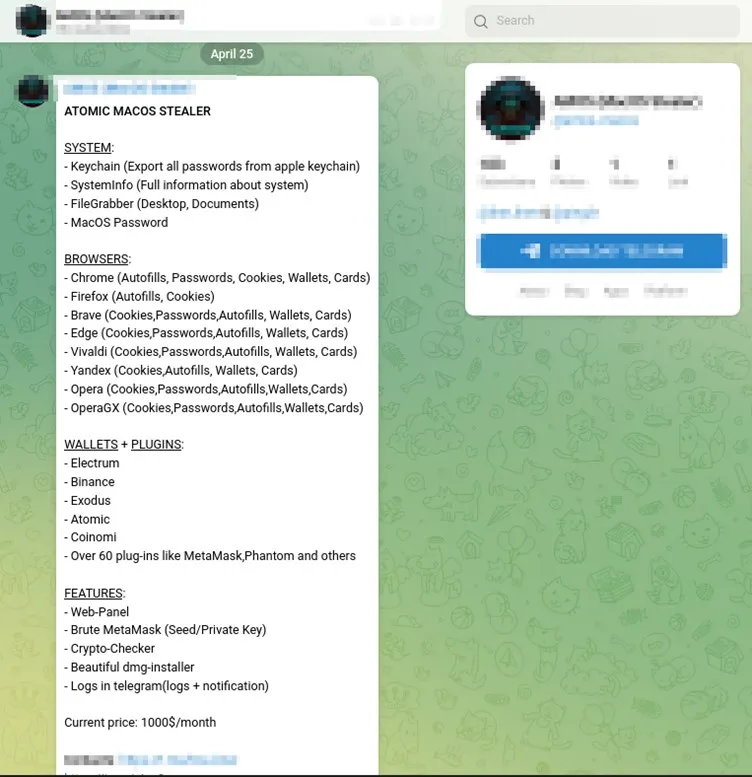
Recently, researchers from Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) discovered a new malware called Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS) that is being promoted in a Telegram channel to steal information. This malware was specifically developed for macOS and can steal sensitive information from the victim’s computer.
The creators of AMOS continually update the malware to make it even more effective. They recently introduced the latest version on Telegram, highlighting its new features.
Once AMOS is installed on a victim’s computer, it can steal a range of information, including keychain passwords, system information, and files from the desktop and documents folder. It can also extract data from various browsers, including autofill data, passwords, cookies, wallets, and credit card information. Cryptocurrency wallets like Electrum, Binance, Exodus, Atomic, and Coinomi are also at risk.
The TA behind AMOS offers additional services, including a web panel for victim management, brute-forcing meta masks to steal seed and private keys, a crypto checker, and a dmg installer, all for the price of $1000 per month.
Due to its robust security features, macOS is the preferred operating system for numerous high-profile individuals. The attack on macOS is not a new trend, and there are various malware families specifically targeting this operating system for infiltration.
Malware like the Atomic macOS Stealer could be installed by exploiting vulnerabilities or hosting on phishing websites. Threat actors can use the stolen data for espionage or financial gain. While not everyday occurrences, macOS malwares can have devastating impacts on victims.
We recommend our readers to follow the best practices below:
#PRVCYTips
- Download and install software only from the official Apple App Store.
- Use secure passwords and employ multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Enable biometric security features such as fingerprint or face recognition for unlocking the device wherever possible.
- Be cautious when opening links received via email.
- Be careful when granting permissions.
Keep your devices, operating systems, and applications up to date.